 |
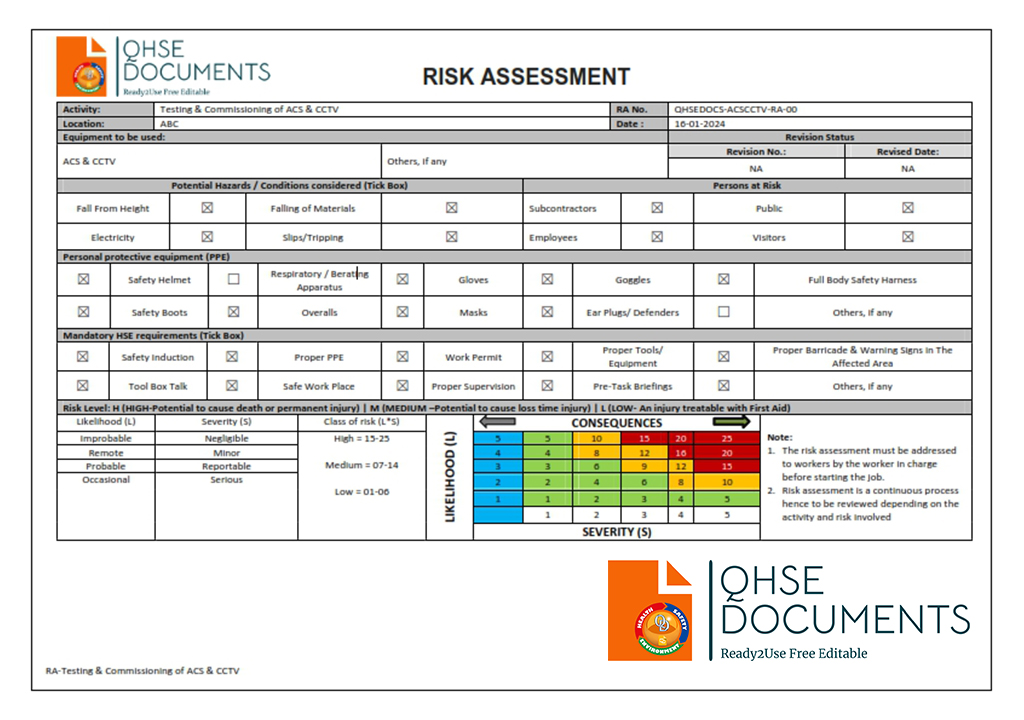
| GENERAL RISK ASSESSMENT-TESTING & COMMISSIONING OF ACCESS CONTROL SYSTEM (ACS) & CCTV |
This document, uploaded by QHSE Documents, provides a detailed risk assessment for the testing and commissioning of ACS and CCTV systems. Designed for HSE professionals, project managers, engineers, and supervisors, it identifies potential hazards, evaluates risks, and outlines control measures to ensure safety during these activities. Available in an editable, ready-to-use Word format, this resource supports compliance with health, safety, and environmental standards, helping teams efficiently mitigate risks and uphold project safety objectives. QHSE Documents offers this and other HSE resources for free download, catering to global safety professionals.
1.0. Task
- Workers
- Scaffold
- Ladder
- Heavy Machinery
- Usage of tools/equipment
2.0. Hazard
A.
- Falling from height
- Falling objects
- Electrocution
- Burns
B.
- Scaffold Collapse
- Overloaded
- Vertigo while working at a height
- Falling of tools/equipment
C.
- Ladder slippage
D.
- Defective/damaged machinery
- Improper handling
- Misuse
E.
- Defective/damaged tools
- Improper handling
- Misuse
3.0. List of Risk (s) Associated
- Falling from Height
- Severe injuries or fractures.
- Permanent disability or fatality.
- Loss of productivity and downtime.
- Falling Objects
- Head injuries or trauma.
- Damage to equipment or property.
- Risk of fatality in severe cases.
- Electrocution
- Cardiac arrest or severe burns.
- Nerve damage or neurological impact.
- Risk of fire or explosion.
- Burns
- Skin tissue damage or scarring.
- Infections due to open wounds.
- Long-term physical or psychological impact.
- Structural failure leads to worker falls. Consequence: Severe injuries or fatalities.
- Damage to nearby equipment or materials.
- Operational delays and financial loss.
- Falling debris from collapse.
- Injuries to personnel below.
- Scaffold instability due to excess weight.
- Collapse causing multiple injuries.
- Equipment damage from weight stress.
- Repair or replacement costs.
- Material falling off scaffold.
- Injuries to workers or bystanders.
- Loss of balance or consciousness.
- Falls cause serious injuries.
- Delayed work response due to dizziness. Increased risk of accidents.
- Inability to safely operate tools.
- Harm to self or others.
- Tools slipping from grip or storage.
- Head injuries to workers below.
- Damage to equipment or structures.
- Costly repairs or replacements.
- Workflow interruption.
- Reduced productivity and project delays.
- Leads to severe injuries like fractures or head trauma.
- Causes equipment or materials to fall, resulting in property damage or harm to others.
- Results in entrapment or crushing injuries.
- Increased risk of equipment failure causing injuries.
- Potential for fire or electrical hazards.
- Decreased productivity and costly repairs.
- Risk of musculoskeletal injuries or strains.
- Dropped loads leading to property damage.
- Potential harm to nearby workers.
- Overloading machinery causes breakdowns or accidents.
- Inappropriate tool usage leads to operator injury.
- Damage to equipment, resulting in operational delays.
- Potential for electrical shocks or mechanical failures.
- Reduced productivity and equipment damage.
- Strains, sprains, or fractures from incorrect lifting techniques.
- Dropping heavy tools may cause injuries or material damage.
- Reduced tool lifespan due to wear and tear.
- Accidental injuries due to tools being used incorrectly.
- Damage to materials or equipment from improper application.
- Potential fires or hazards when tools are misapplied in unsafe conditions.
3.0. Person at Risk
A.
- The person working at a height and below
- Person working below
- The person on or in the vicinity of the power panel
B.
- Any person on or in the vicinity of the scaffold
C.
- Any person on or in the vicinity of the ladder
D.
- All area
E.
- Any person in or in the vicinity of the working area
4.0. Control
A.
- Only approved ladders and heavy machinery are to be provided.
- To work within perimeters of safety.
- Working area to be clean and visual inspection to be done before the start of work.
- Only competent personnel are to be engaged in the task.
- To work within perimeters of safety.
- Working area to be clean and visual inspection to be done before the start of work.
- Only competent personnel are to be engaged in the task.
- Ensure adequate support.
- Defective equipment should not be used.
- Only competent personnel are to be engaged in the task.
- All personnel involved shall be informed of safety, health, and environmental issues.
- Appropriate safety PPE when necessary shall be provided.
- Appropriate safety signboards when necessary shall be provided.
B.
- Sizing of the scaffolding to be properly done as per the expected load.
- To work within perimeters of safety.
- Working area to be clean and visual inspection to be done before starting work.
C.
- Aluminium ladder (2 – 3 meters) to be used only.
- The ladder is to be placed properly on the floor at the proper angle.
- To work within perimeters of safety.
- The working area is to be cleaned and a visual inspection is to be done before the start of work.
- Ensure adequate support.
D.
- Only approved heavy machinery is to be provided.
- Provide adequate manpower support for lifting heavy loads, signalling, and operating.
- Deploy a competent operator to engage in the task.
- To work within perimeters of safety.
E.
- Appropriate tools, equipment and power extension cables are to be used.
- Deploy competent personnel to engage in the task.
- The working area is to be cleaned and visual inspection is to be done before the start of work.